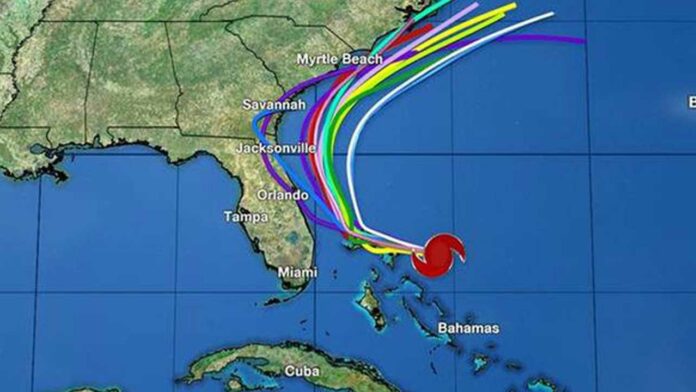
Introduction to Hurricane Spaghetti Models
In recent years, the term “hurricane spaghetti models” has become increasingly common during hurricane season. These models play a crucial role in understanding and predicting the path of hurricanes, aiding in preparedness efforts and decision-making for individuals, communities, and emergency management agencies.
What Are Hurricane Spaghetti Models?
Hurricane spaghetti models refer to a collection of various weather forecast models that predict the potential path a hurricane might take. The term “spaghetti” comes from the visual representation of these models, which often resemble a tangled web of lines resembling strands of spaghetti.
Understanding the Concept
Hurricane spaghetti models combine the outputs of different forecasting models, each with its own set of algorithms and data inputs, to create a comprehensive outlook of possible storm tracks.
Origin of the Term Spaghetti Models
The term “spaghetti models” gained popularity among meteorologists and the public due to the chaotic and intricate appearance of the lines on forecasting maps, resembling a bowl of tangled spaghetti.
How Hurricane Spaghetti Models Work
Hurricane spaghetti models work by aggregating data from multiple sources, including satellites, weather balloons, buoys, and aircraft reconnaissance, into sophisticated computer models. These models then generate a range of possible paths or tracks for the hurricane.
Incorporating Various Weather Forecast Models
Hurricane spaghetti models integrate predictions from various forecasting models, such as the Global Forecast System (GFS), the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), and the National Hurricane Center (NHC) models.
Generating a Range of Possible Paths
By combining multiple forecasts, spaghetti models produce a range of potential paths, accounting for uncertainties in atmospheric conditions and other variables.
Why Are Hurricane Spaghetti Models Used?
Hurricane spaghetti models serve several important purposes in hurricane forecasting and preparedness efforts.
Providing a Visual Representation
The visual representation of hurricane spaghetti models helps stakeholders, including emergency managers, policymakers, and the public, understand the potential trajectory of a storm.
Enhancing Preparedness and Decision-Making
By providing insight into the possible paths a hurricane may take, spaghetti models enable individuals and communities to make informed decisions about evacuation, resource allocation, and other preparedness measures.
Interpreting Hurricane Spaghetti Models
While hurricane spaghetti models are valuable tools, interpreting them requires an understanding of their limitations and uncertainties.
Analyzing the Uncertainty Factor
It’s essential to recognize that hurricane spaghetti models are not definitive predictions but rather probabilistic forecasts that indicate potential storm tracks within a cone of uncertainty.
Identifying the Cone of Uncertainty
The cone of uncertainty represents the range of possible tracks for a hurricane, with the forecasted path typically lying somewhere within this cone.
Factors Affecting Hurricane Tracks
Several factors influence the track of a hurricane, making forecasting a complex and challenging endeavor.
Benefits of Hurricane Spaghetti Models
Hurricane spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecast models, offer several benefits for understanding and predicting the behavior of hurricanes:
Visualization of Uncertainty
Spaghetti models provide a visual representation of the range of possible tracks a hurricane may take. This helps meteorologists and emergency management officials communicate the uncertainty associated with hurricane forecasting to the public more effectively.
Ensemble Forecasting
Spaghetti models are based on ensemble forecasting, which involves running multiple simulations with slight variations in initial conditions and model parameters. By averaging these simulations, forecasters can generate a more comprehensive understanding of possible outcomes, accounting for uncertainties in the atmosphere and model physics.
Identification of Consensus and Outliers
Spaghetti models allow forecasters to identify areas of agreement among different forecast simulations (consensus tracks) as well as outliers that diverge significantly from the consensus. This information helps refine forecasts and assess the likelihood of various scenarios.
Evaluation of Forecast Confidence
By examining the clustering or dispersion of spaghetti model tracks, forecasters can gauge their confidence in a particular forecast. Tight clustering suggests higher confidence, while widely dispersed tracks indicate greater uncertainty.
Assessment of Potential Impacts
Spaghetti models not only show the possible paths of a hurricane but also help evaluate potential impacts such as storm surge, wind, and rainfall along each track. This information is crucial for emergency preparedness and decision-making.
Improvement of Forecast Accuracy
Incorporating ensemble forecasting techniques, including spaghetti models, has contributed to improvements in hurricane track forecasts over the years. By considering a broader range of possible scenarios, forecasters can make more informed predictions and refine their forecasts as new data becomes available.
Public Awareness and Preparedness
Spaghetti models, often shared through various media platforms, raise public awareness about the potential risks associated with hurricanes. This increased awareness can encourage individuals and communities to take proactive measures to prepare for severe weather events, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
Limitations of Hurricane Spaghetti Models
Hurricane spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecast models, have several limitations:
Uncertainty
While spaghetti models provide a range of possible tracks for a hurricane, they don’t offer a definitive prediction. The paths can vary widely among different models, reflecting the inherent uncertainty in predicting the behavior of complex meteorological systems.
Initial Conditions
Spaghetti models heavily rely on initial data inputs, such as current atmospheric conditions and sea surface temperatures. Small errors in these initial conditions can lead to significant divergence in predicted tracks over time.
Model Variability
Different meteorological models may produce divergent results due to variations in their algorithms, grid resolutions, and parameterizations. This variability can make it challenging to assess the most likely path of a hurricane.
Environmental Factors
Spaghetti models typically focus on the hurricane itself and may not fully account for the influence of external factors such as upper-level winds, atmospheric pressure systems, or land interactions. These factors can significantly affect the actual path and intensity of a hurricane.
Limited Forecast Range
Spaghetti models are most reliable within a relatively short forecast range, typically up to five to seven days. Beyond this timeframe, the uncertainty increases substantially, making long-term predictions less accurate.
Model Consistency
The consistency of spaghetti models can vary over time. Some models may consistently overestimate or underestimate certain aspects of a hurricane’s behavior, leading to biases in the predictions.
Complexity
Interpreting spaghetti models requires expertise in meteorology and statistical analysis. Misinterpretation of the data or failure to consider the inherent uncertainties can lead to inaccurate conclusions about the potential impacts of a hurricane.
Evolution of Hurricane Forecasting
The evolution of hurricane forecasting has been a remarkable journey marked by advancements in technology, understanding of atmospheric dynamics, and the development of sophisticated models. Over the years, several key milestones have shaped the way we predict and prepare for these powerful storms.
Examples of Notable Hurricane Spaghetti Model Forecasts
Certainly! “Spaghetti models” refer to graphical representations of various forecast models’ predictions for the track of a hurricane. Here are some notable examples:
Hurricane Irma (2017)
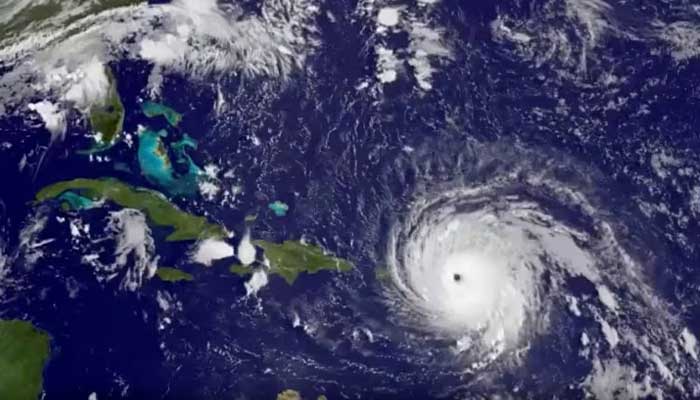 The spaghetti models for Irma depicted a wide range of possible tracks as it moved through the Atlantic Ocean. Initially, there was uncertainty whether it would make landfall in Florida or move up the East Coast, leading to intense monitoring and preparations along the southeastern United States.
The spaghetti models for Irma depicted a wide range of possible tracks as it moved through the Atlantic Ocean. Initially, there was uncertainty whether it would make landfall in Florida or move up the East Coast, leading to intense monitoring and preparations along the southeastern United States.
Hurricane Harvey (2017)
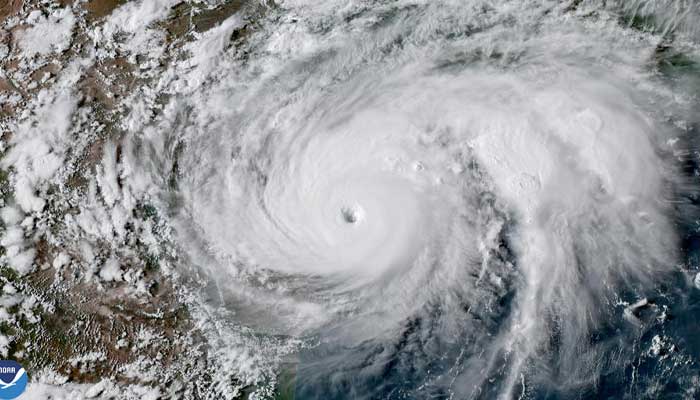 Before making landfall in Texas, Harvey’s spaghetti models showed a divergence in paths, with some models predicting a direct hit on Houston while others suggested a more northerly or southerly track. This uncertainty made it challenging for authorities to issue accurate evacuation orders.
Before making landfall in Texas, Harvey’s spaghetti models showed a divergence in paths, with some models predicting a direct hit on Houston while others suggested a more northerly or southerly track. This uncertainty made it challenging for authorities to issue accurate evacuation orders.
Hurricane Katrina (2005)
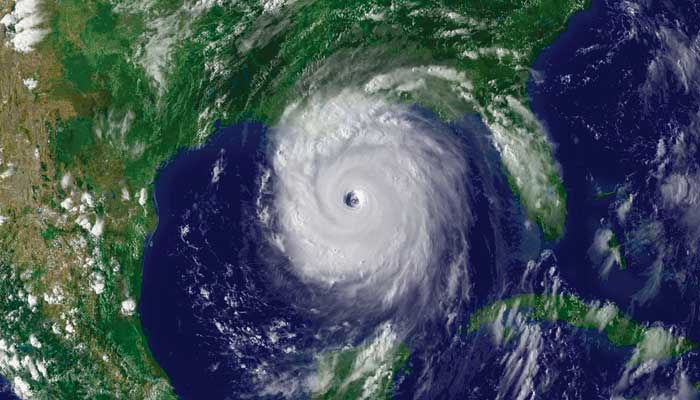 Katrina’s spaghetti models famously showed a variety of potential paths, including scenarios where it could strike New Orleans directly or veer to the east or west. Unfortunately, the actual track led to devastating consequences for New Orleans when the storm breached the city’s levee system.
Katrina’s spaghetti models famously showed a variety of potential paths, including scenarios where it could strike New Orleans directly or veer to the east or west. Unfortunately, the actual track led to devastating consequences for New Orleans when the storm breached the city’s levee system.
Hurricane Sandy (2012)
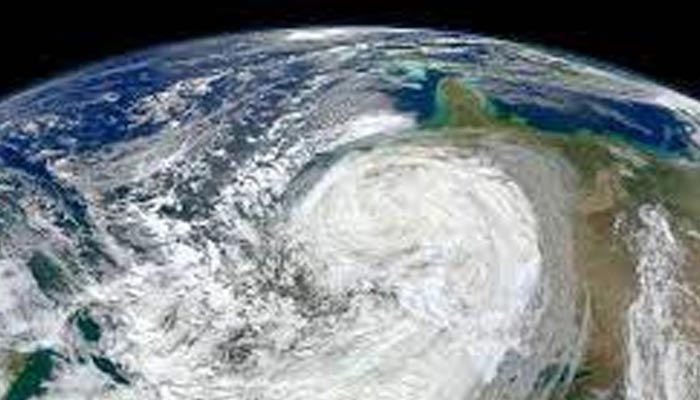 As Sandy approached the East Coast of the United States, spaghetti models indicated the potential for an unusual track that would bring it inland rather than recurving harmlessly into the North Atlantic. This unexpected trajectory contributed to the storm’s historic impact on the Northeast, including widespread power outages and flooding.
As Sandy approached the East Coast of the United States, spaghetti models indicated the potential for an unusual track that would bring it inland rather than recurving harmlessly into the North Atlantic. This unexpected trajectory contributed to the storm’s historic impact on the Northeast, including widespread power outages and flooding.
Hurricane Maria (2017)
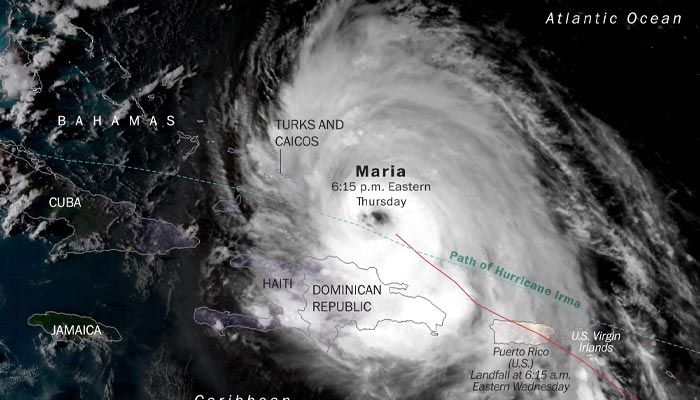 Maria’s spaghetti models initially showed a range of potential paths across the Caribbean, leading to uncertainty about which islands would be most affected. Ultimately, the storm devastated Puerto Rico with its direct hit, causing widespread destruction and a humanitarian crisis.
Maria’s spaghetti models initially showed a range of potential paths across the Caribbean, leading to uncertainty about which islands would be most affected. Ultimately, the storm devastated Puerto Rico with its direct hit, causing widespread destruction and a humanitarian crisis.
These examples highlight the importance of closely monitoring spaghetti models and understanding the uncertainty inherent in hurricane forecasting, as even small variations in a storm’s track can have significant impacts on affected areas.
How Individuals and Communities Can Use Hurricane Spaghetti Models
The evolution of hurricane forecasting has been a remarkable journey marked by advancements in technology, understanding of atmospheric dynamics, and the development of sophisticated models. Over the years, several key milestones have shaped the way we predict and prepare for these powerful storms.
Early Observations
Before the modern era of forecasting, hurricane prediction relied heavily on observations from ships at sea and rudimentary weather instruments. These observations provided limited data and often failed to accurately predict the track and intensity of hurricanes.
Satellite Technology
The launch of weather satellites in the 1960s revolutionized hurricane tracking. Satellites provided continuous, high-resolution imagery of storms from space, allowing forecasters to monitor their development, movement, and structure in real-time.
Radar Systems
Ground-based radar systems, such as Doppler radar, became crucial tools for tracking hurricanes as they approached land. Radar provided detailed information about a storm’s internal structure, including rainfall rates, wind speeds, and the presence of tornadoes within the storm.
Computer Models
The advent of computer modeling in the latter half of the 20th century enabled forecasters to simulate the complex interactions of the atmosphere, ocean, and land. These models became increasingly sophisticated over time, incorporating more data and improving their ability to forecast the track, intensity, and impacts of hurricanes.
Ensemble Forecasting
Ensemble forecasting, which involves running multiple simulations with slight variations in initial conditions, emerged as a valuable technique for quantifying forecast uncertainty. By generating a range of possible outcomes, ensemble forecasts help forecasters assess the likelihood of different scenarios and improve the reliability of predictions.
Data Assimilation
Advances in data assimilation techniques have allowed forecast models to incorporate a wide array of observational data, including satellite, radar, aircraft, and ground-based measurements. Assimilating this data in real-time improves the accuracy of initial conditions, leading to more reliable forecasts.
High-Performance Computing
The exponential growth in computing power has enabled the development of higher-resolution forecast models capable of simulating smaller-scale features within hurricanes. High-performance computing resources also facilitate faster model runs, allowing forecasters to produce timely predictions during rapidly evolving weather situations.
Improvements in Track and Intensity Forecasting
Through continuous research and development, forecasters have made significant strides in both track and intensity forecasting. While track forecasts have become increasingly accurate over the years, intensity forecasting remains challenging due to the complex interactions between hurricanes and their surrounding environment.
Future Trends in Hurricane Forecasting
Hurricanes are among the most destructive natural disasters, causing widespread devastation to coastal communities and posing significant risks to life and property. Accurate forecasting of these powerful storms is crucial for timely evacuation efforts, disaster preparedness, and mitigation strategies. In recent years, advancements in technology and research have led to significant improvements in hurricane forecasting capabilities. This article explores the future trends shaping the field of hurricane forecasting and the potential impact of these developments.
Case Study: Impact of Hurricane Spaghetti Models on Decision-Making
Impact on Decision-Making
Meteorologists heavily rely on spaghetti models to forecast the trajectory of hurricanes accurately. By analyzing various model outputs, they can better understand the range of possible scenarios and make informed predictions. Additionally, these models influence critical decisions regarding evacuation orders. Local authorities use the projected paths to determine which areas are at the greatest risk and need to evacuate.
During emergencies, such as hurricanes, decision-making becomes even more critical. Emergency services must allocate resources effectively and plan for potential scenarios. Spaghetti models provide valuable information that helps authorities prepare for the storm’s impact and respond promptly to mitigate risks.
Case Studies
Several notable case studies highlight the significance of spaghetti models in decision-making during hurricanes. For instance, during Hurricane Irma in 2017, the National Hurricane Center utilized spaghetti models to accurately predict the storm’s path, allowing authorities to issue timely evacuation orders. Similarly, during Hurricane Harvey in 2017, emergency responders used spaghetti models to anticipate flooding and deploy resources accordingly.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their utility, spaghetti models have inherent uncertainties. The varying outcomes displayed by different models can sometimes lead to confusion and indecision among the public. Moreover, the complexity of these models makes them challenging to interpret for non-experts, potentially leading to misinterpretation and panic.
Improvements and Future Directions
Advances in modeling technology continue to improve the accuracy of spaghetti models. High-performance computing and sophisticated algorithms enable meteorologists to generate more precise forecasts, reducing uncertainties. Additionally, efforts to enhance communication strategies aim to make these complex models more accessible to the general public, promoting better understanding and preparedness.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Hurricane Spaghetti Models
Misconception 1: Spaghetti Models Predict Exact Paths
One common misconception is that spaghetti models predict the exact path a hurricane will follow. In reality, these models provide a range of potential paths based on various atmospheric conditions. Hurricanes are complex systems influenced by multiple factors, making it impossible to pinpoint an exact trajectory with certainty.
Misconception 2: All Lines Represent Different Scenarios
Another misconception is that each line in a spaghetti model represents a distinct scenario. While each line does depict a potential track, they are not necessarily separate scenarios. Instead, they represent variations within the model’s forecast, accounting for uncertainties in factors like wind speed, pressure systems, and atmospheric conditions.
Misconception 3: The More Lines, the More Certain the Prediction
Some individuals believe that the more lines present in a spaghetti model, the more certain the prediction. However, the density of lines does not indicate forecast certainty. Instead, it reflects the variability and uncertainty inherent in predicting the path of a hurricane. A higher density of lines signifies a greater range of potential outcomes, highlighting the complexity of forecasting.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, hurricane spaghetti models serve as invaluable tools in the realm of weather forecasting, providing vital insights into the potential paths and intensities of hurricanes and tropical storms. By aggregating the outputs of multiple forecasting models, these spaghetti plots offer a comprehensive view of the uncertainties associated with storm prediction.
Despite their complexity, spaghetti models enhance our ability to anticipate and prepare for extreme weather events, ultimately contributing to the safety and resilience of communities in vulnerable areas. As technology advances and our understanding of atmospheric dynamics improves, we can expect even greater accuracy and reliability in future hurricane forecasts.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
What are the main sources of data used in generating hurricane spaghetti models?
Meteorologists utilize data from various sources, including satellites, weather balloons, ocean buoys, and ground-based weather stations, to collect information about the current state of the atmosphere.
2. How do meteorologists interpret spaghetti models to predict storm tracks?
Meteorologists analyze the ensemble of forecasts generated by spaghetti models to identify common trends and outliers, helping them determine the most likely path of the storm.
3. Are spaghetti models always accurate in predicting the path of hurricanes and tropical storms?
While spaghetti models offer valuable guidance, they are not infallible, and uncertainties still exist. Factors such as atmospheric conditions and model limitations can affect the accuracy of predictions.
4. What are some limitations of spaghetti models in hurricane forecasting?
Spaghetti models can be challenging to interpret, and there is a potential for misinterpretation by the general public. Additionally, uncertainties in initial conditions and model assumptions can affect the reliability of forecasts.
5. How can communities use spaghetti models to prepare for hurricanes and tropical storms?
Communities can use spaghetti models to better understand the potential threats posed by hurricanes and tropical storms, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding evacuation, emergency preparedness, and resource allocation.